
[GN Vol.5 No.2] Popular Articles and Research Trend
작성자
관리자작성일자
2023-12-29 00:00조회수
69카테고리
Popular Articles and Research Trend
Popular Articles and Research Trend
by Taewoon Kim, Pusan National University,
South Korea
One effective way
to identify the recent research directions and trends is to pay attention to
the most popular research papers published recently. This article reviews such
most accessed and downloaded papers in Journal of Communications and Networks
(JCN) and Information & Communications Technology Express (ICT Express),
both of which are published by The Korean Institute of Communications and
Information Sciences (KICS).
<JCN>
Paper
|
W. Kim
et al., “Towards deep learning-aided wireless channel estimation and channel
state information feedback for 6G,” vol. 25, no. 1, Feb. 2023.
|
doi
| https://doi.org/10.23919/JCN.2022.000037
|
Abstract
|
Deep learning (DL), a branch of
artificial intelligence (AI) techniques, has shown great promise in various disciplines
such as image classification and segmentation, speech recognition, language
translation, among others. This remarkable success of DL has stimulated
increasing interest in applying this paradigm to wireless channel estimation
in recent years. Since DL principles are inductive in nature and distinct
from the conventional rule-based algorithms, when one tries to use DL
technique to the channel estimation, one might easily get stuck and confused
by so many knobs to control and small details to be aware of. The primary
purpose of this paper is to discuss key issues and possible solutions in
DL-based wireless channel estimation and channel state information (CSI)
feedback including the DL model selection, training data acquisition, and
neural network design for 6G. Specifically, we present several case studies
together with the numerical experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness of
the DL-based wireless channel estimation framework.
|
Paper
|
S. Subbiah
et al., “Intrusion detection technique in wireless sensor network using grid
search random forest with Boruta feature selection algorithm,” vol. 24, no. 2,
Apr. 2022.
|
doi
| https://doi.org/10.23919/JCN.2022.000002
|
Abstract
|
Attacks in wireless sensor networks
(WSNs) aim to prevent or eradicate the network's ability to perform its
anticipated functions. Intrusion detection is a defense used in wireless
sensor networks that can detect unknown attacks. Due to the incredible development
in computer-related applications and massive Internet usage, it is
indispensable to provide host and network security. The development of
hacking technology tries to compromise computer security through intrusion.
Intrusion detection system (IDS) was employed with the help of machine
learning (ML) Algorithms to detect intrusions in the network. Classic ML
algorithms like support vector machine (SVM), K-nearest neighbour (KNN), and
filter-based feature selection often led to poor accuracy and misclassification
of intrusions. This article proposes a novel framework for IDS that can be
enabled by Boruta feature selection with grid search random forest (BFS-GSRF)
algorithm to overcome these issues. The performance of BFS-GSRF is compared
with ML algorithms like linear discriminant analysis (LDA) and classification
and regression tree (CART) etc. The proposed work was implemented and tested
on network security laboratory — knowledge on discovery dataset (NSL-KDD).
The experimental results show that the proposed model BFS-GSRF yields higher
accuracy (i.e., 99%) in detecting attacks, and it is superior to LDA, CART,
and other existing algorithms.
|
<ICT Express>
Paper
|
Y.
Jamtsho et al., “Real-time license plate detection for non-helmeted
motorcyclist using YOLO,” vol. 7, no. 1, Mar. 2021.
|
doi
| https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icte.2020.07.008
|
Abstract
|
Nowadays, detection of license plate (LP)
for non-helmeted motorcyclist has become mandatory to ensure the safety of
the motorcyclists. This paper presents the real-time detection of LP for
non-helmeted motorcyclist using the real-time object detector YOLO (You Only
Look Once). In this proposed approach, a single convolutional neural network
was deployed to automatically detect the LP of a non-helmeted motorcyclist
from the video stream. The centroid tracking method with a horizontal
reference line was used to eliminate the false positive generated by the
helmeted motorcyclist as they leave the video frames. The overall LP
detection rate was 98.52%.
|
Paper
|
A. Sen
et al., “Categorization of actions in soccer videos using a combination of
transfer learning and Gated Recurrent Unit,” vol. 8, no. 1, Mar. 2022.
|
doi
| https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icte.2021.03.004
|
Abstract
|
Extraction of knowledge from soccer
videos has enormous applications like context-based advertisement,
content-based video retrieval, match summarization, and highlight extraction.
Overlapping soccer actions and uncontrolled video capturing conditions make
it challenging to detect action accurately. For overcoming these problems,
Convolutional Neural Network and Recurrent Neural Network are used jointly to
classify different lengths of soccer actions. Initially, transfer learning
from pre-trained VGG network extracts characteristic spatial features.
Afterwards, Gated Recurrent Unit deals with temporal dependency and solves
the vanishing gradient problem. Finally, softmax layer assigns decimal
probabilities to each class. Experimental results demystify the significance
of the proposed architecture.
|
Machine learning
(ML) and deep learning (DL) techniques are continuously advancing and their
applications have extended to wireless communications and network security and several
other fields. One notable research proposed by Kim et al. showed that deep
learning can be an effective solution to the challenge of wireless channel
estimation in wireless communication. It is well known that channel adaptive
signaling can enhance the performance of wireless communication systems to a large
extent. However, obtaining an accurate knowledge of channel state at the
transmitter is challenging in practice. To address this challenge, especially for future wireless systems
with high-frequency bands,
Kim et al. presented a comprehensive
study on (i) the choice of an
adequate deep learning model, (ii) designing a neural network architecture, and (iii) data
acquisition for training the model.
This article begins with a summary of the conventional and DL-based
approaches for wireless channel estimation. It then discusses commonly arising design issues in DL-based
channel estimation, such as training data
acquisition and design of the neural network architecture. Finally, in the
DL-aided Channel Estimation and Exploration section, the authors explore diverse
neural network models designed to solve the problems of channel estimation. For
example, Fig. 1 shows the proposed LSTM-based parametric channel estimation
model for mmWave/THz MIMO communications.
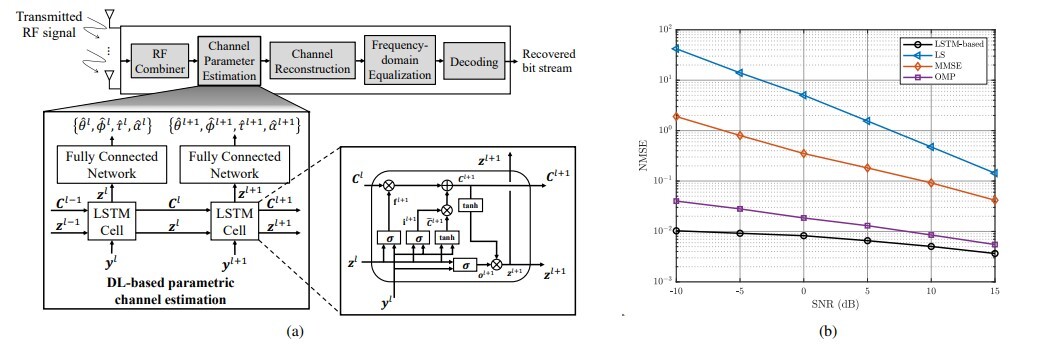
Figure
1. (a) LSTM-based channel estimation (b) Evaluation results [Kim et
al.]
Furthermore, application of grid search and random forest machine learning model to the problem of intrusion detection in wireless sensor networks (WSN) was proposed by Subbiah et al. WSN are widely used networks dedicated to transmitting sensed readings in diverse applications, such as healthcare and manufacturing. Although many applications of WSN carry private and/or confidential information, they are vulnerable to security attacks because they operate in an unattended environment, communicate with each other in a broadcast manner, and are resource-constrained. Thus, to enhance the level of security of WSNs, an intrusion detection system (IDS) is required to protect legitimate user information from attackers.
The use of large-scale WSNs over a long period of time results in a huge dataset that can be effectively handled by ML techniques. Many approaches use ML to enhance the performance of IDS; however, the importance of feature selection has been underestimated. Subbiah et al. proposed an effective feature selection algorithm with grid search and random forest to further enhance IDS for WSNs. The widely used KDDCUP dataset with 490 thousand samples and 42 features was used in their study, and the authors proposed two models that enhance the accuracy of IDS, referred to as Model 1 and Model 2. The proposed Model 1, called BFS-GSRF, uses the Boruta feature selection algorithm to select the features and then runs grid search random forest algorithm for detection classification. The detailed operation of BFS-GSRF is illustrated in Fig. 2. The Model 2, on the contrary, uses the Pearson’s correlation coefficient to select features. It then uses linear discriminant analysis, and classification and regression tree to detect attacks accurately.
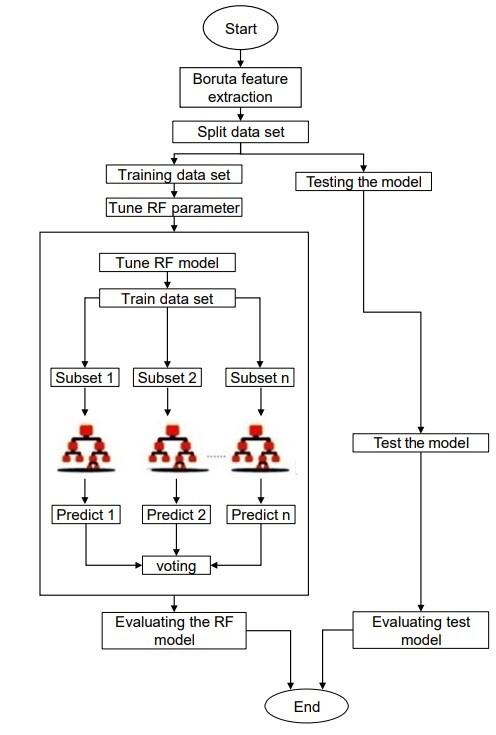
Figure 2. BFS-GSRF algorithm [Subbiah et al.]
In this issue, we chose two papers from ICT Express that introduce the use of well-known DL models in computer vision applications. Jamtsho et al. proposed the use of YOLO v2 to detect the license plates of motorcycles if the driver is not wearing a helmet.
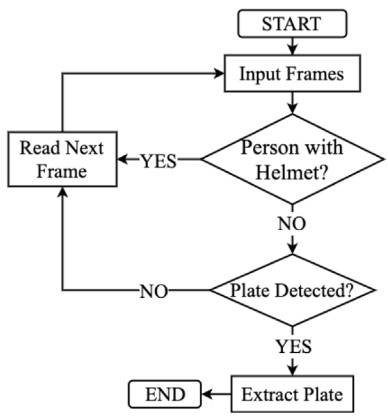
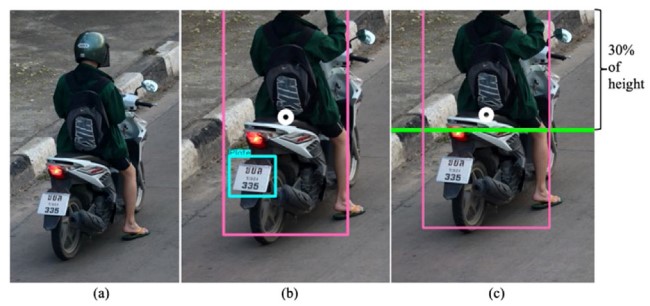
Figure
3. License plate detection [Jamtsho et al.]
Fig. 3 shows the workflow of the proposed approach and its detection results. As shown in the flowchart, when a person is detected in a given image, the proposed approach first searches for a helmet. If the helmet is missing in the image, the next step is to find the license plate. Fig. 3(a) shows that license plate detection was not performed, given the presence of a helmet. Contrarily, Fig. 3(b) shows that the license plate detection step is carried out if the helmet is missing. However, the detection of license plate in Fig. 3(b) may be unnecessary if the helmet is found missing only because the helmet is outside the frame boundaries. To overcome such problems, the authors proposed using the centroid-tracking method that detects the center of a detected human object. If the center is above a predefined threshold, as indicated by the green horizontal line in Fig. 3(c), the proposed approach does not attempt to detect the license plate. This study reports that the overall accuracy of license plate detection was 98.52%.
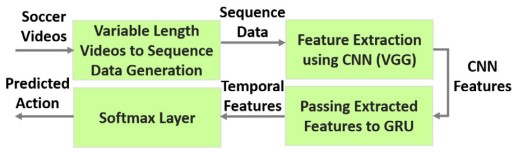
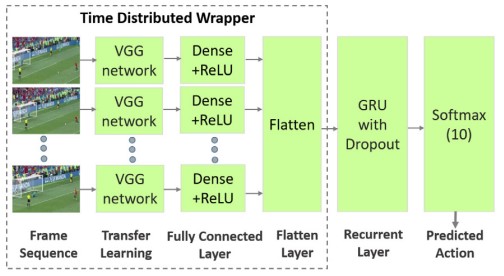
Figure 4. Soccer action categorization (SAC) scheme [Sen et al.]
The main contributions of this work are twofold: First, it uses a pretrained VGG to extract features from the recorded soccer-playing image dataset. Subsequently, using the GRUs, the authors carry out transfer learning was performed to correctly categorize the player’s play. The extensive evaluation results reported in the study suggest that the proposed approach achieves an accuracy of 94%.